Businesses are increasingly considering ChatGPT as an attractive option for improving their customer experience and optimizing their operations.
These AI-powered virtual assistants can be configured to handle a variety of tasks, from answering customer inquiries to processing orders and scheduling appointments. At Top Data Science, we have been closely following the development of large language models (LLMs). In this blog post, we aim to provide some background and helpful guidelines on what to do and what to be aware of when implementing these systems into your business.
Potential use cases
- Public chatbots/automated helpdesk
- Internal knowledge/documentation management
- Risk analysis and reporting
- Prototyping different approaches for implementing solutions to specific user problems
- Data assessment and analysis based on images and text
- Semantic search systems, e.g. in legislation or research
- Automated booking systems
- Code generation and documentation
Background
OpenAI
OpenAI is a US-based artificial intelligence (AI) research laboratory founded in 2015. Its founders included names like Elon Musk (no longer on the board), Ilya Sutskever, Greg Brockman, Sam Altman, and Andrej Karpathy. The organization’s founders pledged $1 billion to the company with a statement of making its future patents and research open to the public. [1] The first four years of the company (2015-2018) were run as a non-profit.
The transition to for-profit happened in 2019 and a partnership with Microsoft was announced, which invested $1 billion in the company. In 2023, Microsoft increased its stake as part of a multi-year investment of $10 billion. [2]
The GPT-models
The original paper on the generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) model was published in 2018 by Alec Radford et al. [3], which was trained on a BookCorpus dataset (4.5 GB), consisting of the text from around 7,000 unpublished books. Unlike other best-performing neural natural language processing (NLP) models at the time, the GPT model was trained using a semi-supervised approach (vs. supervised learning), which removed the need for well-annotated datasets. The GPT model is a type of deep learning model, capable of generating human-like text, e.g. answering questions, summarizing text, translating to other languages, code generation, and generation of content like blogs and poems.
Following the transition to a for-profit organization, OpenAI introduced a series of large language models (LLMs): GPT-2 (2019), GPT-3 (2020), GPT-3.5 (2022), and GPT-4 (2023). Each successive model has been trained using more comprehensive datasets, e.g. the GPT-3 dataset included webpage data, Reddit posts (with 3+ upvotes), books, and Wikipedia pages, worth 45 TB [4]. The dataset for the GPT-4 model has not been made public. The GPT-4 is the first model in the series to be considered a multi-modal model, hence its dataset is likely to have included other types of data than just text, such as images. With every model increment, the number of model parameters has also vastly increased, from 0.12 billion in GPT-1 to 175 billion in GPT-3 [3,4]. Parameters are configuration variables that the model learns during the training process and that in simplistic terms define the “skill” of the model for a particular problem. The number of parameters affects the model’s capacity to perform complicated tasks, akin to how the number of neurons in the brain affects (but does not alone determine) the cognitive capabilities of a live being.
ChatGPT
While the GPT models have paved the way for large language models (LLMs), the introduction of ChatGPT generated a significant amount of media attention. According to OpenAI, over a million signups were received for the first free preview of ChatGPT. [5]
The original ChatGPT model was built by finetuning the GPT-3.5 model using an approach called reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which combines both supervised and reinforcement learning [6] (see Figure 1). In the first step, human trainers created conversations with each other, mimicking the user and an AI assistant. The trainers were given model-written suggestions for responses as a starting point. These dialogues were then used in the first model finetuning dataset. In the second part, comparison data was collected that included two or more model responses, which the human trainers ranked based on their quality. This data was then used to finetune the model using proximal policy optimization (PPO).
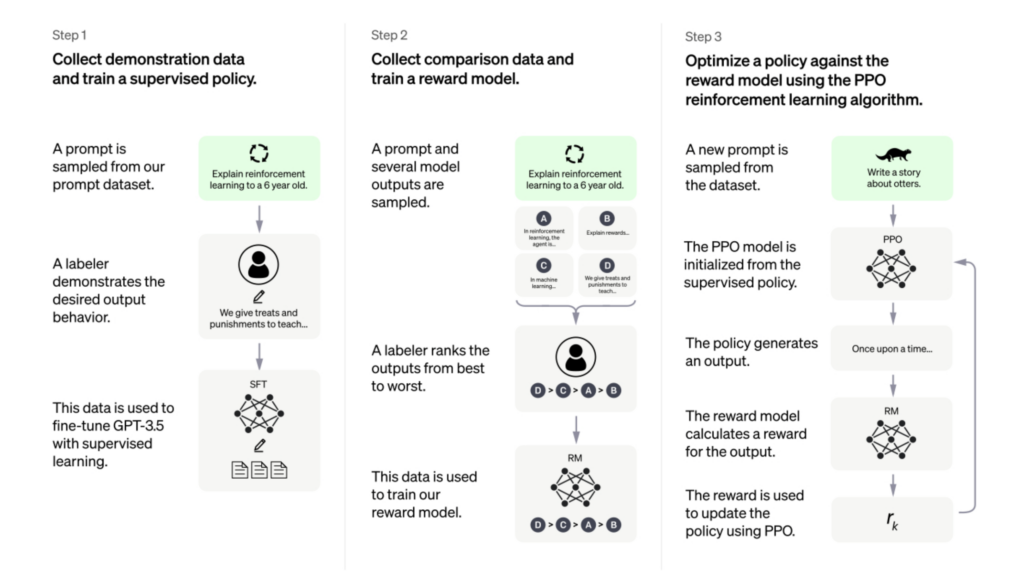
(source: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt)
ChatGPT (GPT-4)
The new GPT-4 model was developed to improve its performance in following user intentions, while also reducing the number of false and offensive outputs (OpenAI refers to this as “alignment”) [7]. The user can now also steer the model in its writing style and tone, e.g. “You are a talkative data science expert”. Another major change with the latest model is that it is the first multimodal model in the series, accepting both text and image inputs. This opens up new possibilities such as caption writing, descriptions of image content and identifying trends seen in plots. A second high impact change is the model’s capability to solve more complex mathematical and scientific problems, as well as providing simple explanations for complex topics.
The recent model announcement was accompanied by a GPT-4 technical report [8]. To many researchers’ disappointment, the report revealed no details about the architecture, model size, hardware, dataset construction, or training method. This was said to be the result of the current competitive landscape and the safety implications of large-scale models.
Integration
ChatGPT is available for integration via the OpenAI Chat API. [9] Currently, the user is able to select the gpt-3.5-turbo or gpt-4 model.
While there is a limited free tier to try the service, the use of ChatGPT via the API is not free. The prices are reported per 1,000 tokens (approximately 750 words). For example, the use of ChatGPT with gpt-3.5-turbo costs $0.002 / 1K tokens as of 27/3/2023. [10]
Data submitted through the API is not used for service improvements (including model training) unless the organization opts in. The data is stored for 30 days to monitor abuse and/or misuse after which it gets deleted. All customer data is processed and stored in the US. OpenAI does not currently store data in Europe or in other countries.
Plugins
A more advanced way of using ChatGPT capabilities was announced with the support of plugins [11]. They allow ChatGPT to access up-to-date information and use third-party services. Currently, there is still a waiting list to get access to this functionality. The first round of companies announcing their plugins included e.g. Klarna, Expedia, and Slack.
Things to be aware of and consider
- Incorrect answers – It is difficult to tell if the model answer is correct unless you have previous knowledge of the topic. Currently the model itself cannot indicate when it doesn’t know or when it’s uncertain about its answer.
- Bias – The training data influences the model’s answers and hence might include bias, e.g. when selecting between certain ethnicity groups.
- Inadequate or missing sources – Depending on how and where the model is being used, there is no way of finding out where the information is coming from (i.e. it cannot cite the original source). This makes it problematic for information retrieval. For example, the model may output an almost perfect copy of a piece of text or code from an unknown source, and one may run the risk of unintentional plagiarism. However, it is worth noting that ChatGPT incorporated into Bing and Edge now includes the original source(s).
- Data privacy and security – Do not input company data into ChatGPT as this will be visible to OpenAI and can be used to further train the model. Instead use the API, which is considered a commercial service.
- Ecological sustainability – running ChatGPT is extremely resource-intensive.
In conclusion, while ChatGPT has shown great potential, it is still in the early stages of adoption. As with any transformative technology, it is important to consider the potential risks and opportunities it presents. Regardless, neglecting the potential upsides could lead to missed benefits and falling behind in the industry. Furthermore, given the legislation has not yet caught up with the rapid pace of advancements in AI, it is crucial to continue evaluating these models and their capabilities to develop appropriate regulations.
If you’re interested to hear more about ChatGPT and how to incorporate it into your business, please don’t hesitate to contact us at Top Data Science. In the next blog post about ChatGPT, we will discuss how to integrate your system with the API.
–
Authors:
Emma Meeus, PhD, Senior Data Scientist
Kai Lehtinen, COO
References
- https://openai.com/blog/introducing-openai
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/qai/2023/01/27/microsoft-confirms-its-10-billion-investment-into-chatgpt-changing-how-microsoft-competes-with-google-apple-and-other-tech-giants/
- Radford, Alec and Karthik Narasimhan. “Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training.” (2018). https://openai.com/research/language-unsupervised.
- Tom B. Brown, Benjamin Mann, Nick Ryder et al. “Language Models are Few-Shot Learners” (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165
- https://www.nytimes.com/2022/12/05/technology/chatgpt-ai-twitter.html
- https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
- https://openai.com/research/gpt-4
- https://cdn.openai.com/papers/gpt-4.pdf
- https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/chat
- https://openai.com/pricing
- https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-plugins




